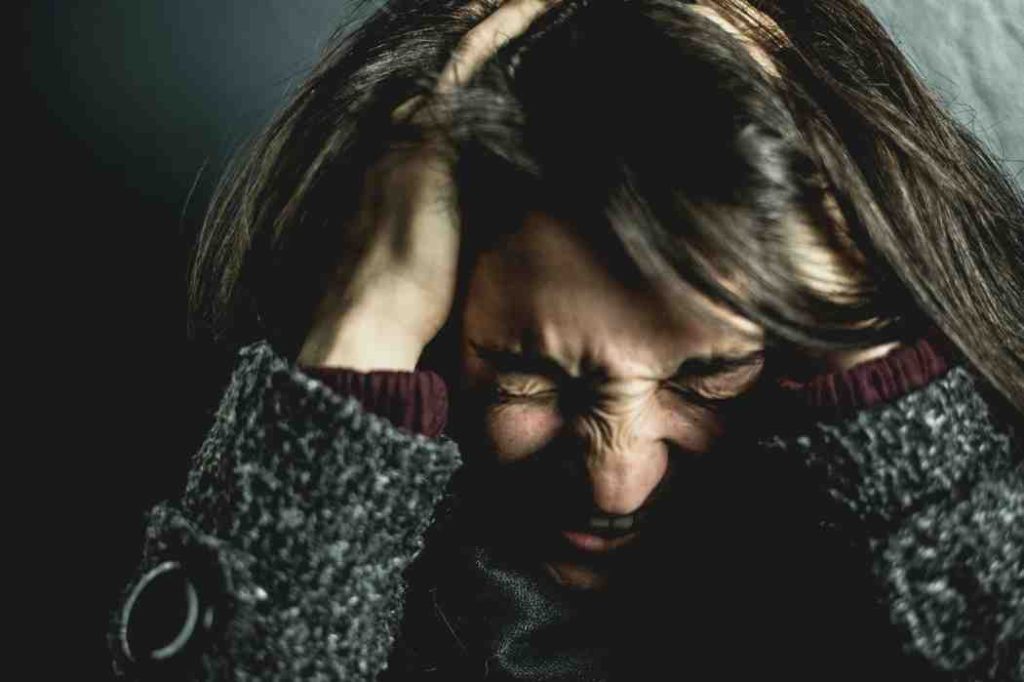
Have you ever had a great night out, only to wake up the next morning feeling anxious and panicked? You’re not alone. This phenomenon is called hangxiety, short for hangover anxiety, and it affects about 22% of social drinkers.
The causes of hangxiety and offers tips for preventing and managing it.
What Causes Hangxiety?
Hangovers are caused by the body’s attempt to recover from alcohol consumption. While dehydration and disrupted sleep contribute to physical symptoms like headaches and nausea, alcohol also has a significant impact on the brain.
- Chemical Imbalance: Alcohol acts as a depressant, altering the levels of neurotransmitters (chemical messengers) in the brain. It increases GABA, making you feel relaxed and uninhibited, and decreases glutamate, slowing down your thoughts.
- The Rebound: As the alcohol wears off, your brain tries to rebalance these chemicals. This shift has the opposite effect, causing your brain to become overstimulated, leading to anxiety.
Why Do Some People Get It More Than Others?
Several factors can influence hangxiety:
- Genetics: Up to half of the reason why you experience hangover symptoms can be linked to your genes. Some people simply process alcohol differently, leading to more intense physical effects that trigger anxiety.
- Drinking Habits: Heavier drinking naturally leads to worse hangovers, including hangxiety.
- Memory Lapses: Waking up with vague memories of the night before can fuel anxiety as you worry about what you might have said or done.
- Underlying Anxiety: People who already struggle with anxiety are more susceptible to hangxiety. They may use alcohol to cope with stress, leading to heavier drinking and a worsened cycle of anxiety.
Preventing Hangxiety:
The best way to avoid hangxiety is to limit your alcohol intake. Australian guidelines recommend no more than 10 standard drinks per week and no more than 4 on any single day. Here are some additional tips:
- Avoid mixing alcohol with other drugs.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the night and before bed.
- Eat before and during drinking: Food helps slow down alcohol absorption.
Dealing With Hangxiety:
If you do wake up feeling anxious, focus on physical recovery:
- Hydrate: Replenish lost fluids with water.
- Eat a light meal: Food can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Rest: Allow your body time to recover.
Managing Anxiety:
- Mindfulness or deep breathing: These can help calm your mind and racing thoughts.
- Journaling: Writing down your anxieties can help you process them and gain perspective.
- Talk to a friend: Sharing your worries can provide support and reduce feelings of isolation.
Understanding hangxiety can help you manage it and make those mornings after a night out a little less stressful.